Write a blog post explaining the role of FACTS in enhancing the stability and reliability of electrical grids. Describe the various FACTS devices, including Static Var Compensation (SVC) Thyristor Controlled Series Compensatoes (CSC), Stanc Phase Shifters (SPS), Static Condensers (STATCON), Static Synchronous Series Compensators (SSSC), and Unified Power Flow Commlers (UPFC) Descuss how these devices contribute to grid optimization and power quality.
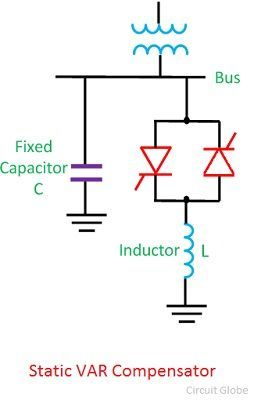
Static Var Compensation (SVC) A static VAR compensator is a parallel combination of controlled reactor and fixed shunt capacitor shown in the figure below. The thyristor switch assembly in the SVC controls the reactor. The firing angle of the thyristor controls the voltage across the inductor and thus the current flowing through the inductor. In this way, the reactive power draw by the inductor can be controlled. The SVC is capable of step less adjustment of reactive power over an unlimited range without any time delay. It improves the system stability and system power factor. Most commonly used SVC scheme are as follows. Thyristor controlled reactor (TCR) Thyristor-switched capacitor (TSC) Self Reactor (SR) Thyristor controlled reactor – Fixed capacitor (TCR-FC) Thyristor-switched capacitor – Thyristor controlled reactor (TSC-TCR) Advantage of Static VAR Compensator It increased the power transmission capability of the transmission lines. It improved the transient stability ...
